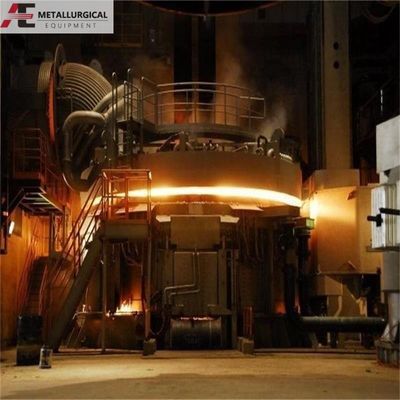
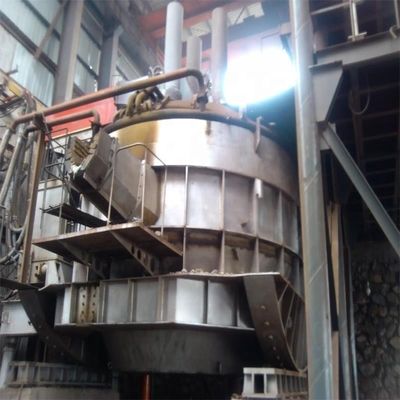
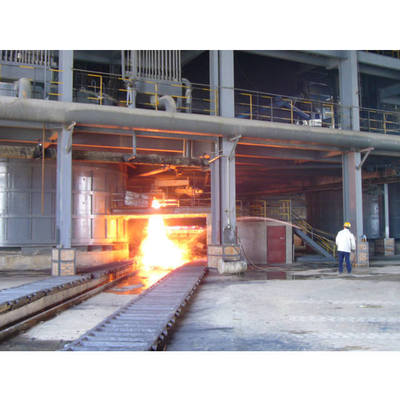
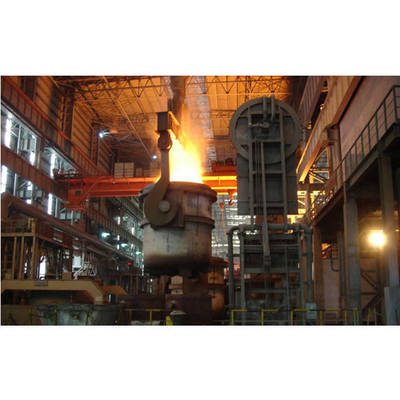
Perbandingan Tungku Busur Listrik DC dan Tungku Busur Listrik AC Tradisional
Tungku busur listrik adalah alat penting untuk pembuatan baja, tersedia dalam berbagai konfigurasi. Di antara ini, tungku busur listrik DC (Arus Searah) adalah pengembangan signifikan yang berasal dari jenis AC (Arus Bolak-balik) yang lebih umum. Jadi, apa saja keunggulan tungku busur listrik DC? Artikel ini menguraikan manfaat utamanya dibandingkan dengan tungku AC tradisional.
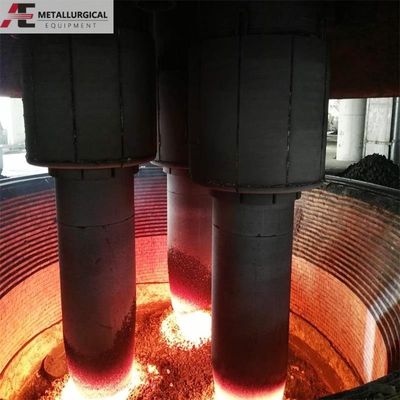
Tungku busur listrik DC adalah wadah pembuatan baja yang menggunakan catu daya arus searah. Seperti pasangannya AC, ia menghasilkan panas dari busur listrik yang terbentuk antara elektroda dan muatan (atau bak cair) untuk melakukan peleburan, cocok untuk memproduksi baja dan berbagai paduan.
Keunggulan Utama Tungku Busur Listrik DC dibandingkan Tungku AC Tradisional:
1. Busur yang Stabil dan Terkonsentrasi: Busur DC lebih stabil dan terfokus. Hal ini meningkatkan pengadukan bak yang lebih baik, mengarah pada distribusi suhu yang lebih seragam di dalam tungku, dan menghasilkan pengurangan keausan pada lapisan tahan api.
2. Pengurangan Gangguan Listrik: Fluktuasi arus dan tegangan jauh lebih kecil. Hal ini meminimalkan dampak pada jaringan listrik (mengurangi kedipan dan harmonik) dan dapat memperpanjang umur operasional kabel listrik terkait.
3. Konsumsi Elektroda yang Lebih Rendah: Kehilangan elektroda jauh lebih sedikit. Konsumsi elektroda per ton baja bisa mencapai 50% lebih rendah dibandingkan dengan tungku busur listrik AC.
Terlepas dari keunggulan kinerja ini, adopsi tungku busur DC secara luas secara historis dibatasi oleh tantangan untuk mendapatkan catu daya DC berdaya tinggi yang andal. Hambatan teknis ini menghambat pengembangan mereka selama bertahun-tahun.
Kemajuan teknologi thyristor (semikonduktor daya) pada akhir tahun 1970-an akhirnya memungkinkan pembuatan sistem penyearah DC berdaya tinggi yang kuat. Terobosan ini memperbarui minat industri dan mengarah pada penyelesaian tantangan desain dan operasional utama untuk tungku busur DC pada awal tahun 1980-an.
Perbedaan Operasional Utama:
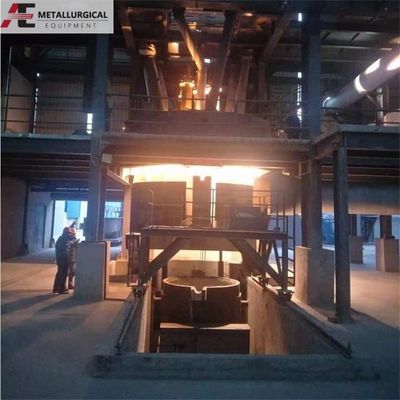
Perbedaan mendasar terletak pada konfigurasi elektroda. Tungku busur DC biasanya menggunakan satu elektroda grafit sebagai katoda (terminal negatif), sedangkan bagian bawah tungku bertindak sebagai anoda (terminal positif).
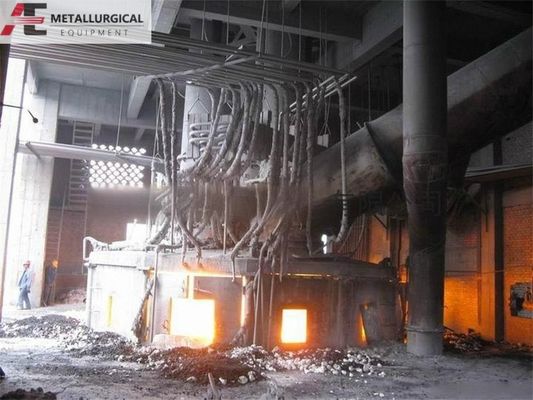
Sistem Catu Daya: Sistem kelistrikan berbeda dari tungku AC. Ini termasuk penyearah untuk mengubah AC menjadi DC dan reaktor untuk menstabilkan busur. Jalur arus balik diselesaikan melalui elemen konduktif, atau "kontak," yang dipasang di perapian tungku.
Aspek Operasional Kritis: Desain, pemeliharaan, dan umur panjang kontak bawah ini sangat penting untuk pengoperasian tungku DC yang andal. Konfigurasi umum melibatkan penempatan pelat tembaga pada pelat baja bagian bawah tungku untuk konduktivitas. Ini biasanya ditutupi oleh tiga lapisan bata magnesia-karbon, di mana lapisan perapian tahan api standar ditumbuk atau dipasang.
Kami adalah produsen tungku listrik profesional. Untuk pertanyaan lebih lanjut, atau jika Anda memerlukan tungku busur terendam, tungku busur listrik, tungku pemurnian wadah, atau peralatan peleburan lainnya, jangan ragu untuk menghubungi kami di susan@aeaxa.com

 Pesan Anda harus antara 20-3.000 karakter!
Pesan Anda harus antara 20-3.000 karakter! Silakan periksa email Anda!
Silakan periksa email Anda!  Pesan Anda harus antara 20-3.000 karakter!
Pesan Anda harus antara 20-3.000 karakter! Silakan periksa email Anda!
Silakan periksa email Anda! 








